How netarsudil works to lower IOP
The problem of reduced outflow
In open-angle glaucoma patients, IOP becomes elevated when the trabecular meshwork becomes fibrotic and aqueous humor outflow is reduced.1
- The trabecular meshwork is integral to the regulation of aqueous humor outflow and IOP2
- Cellular damage due to glaucoma (eg, oxidative stress) may result in stiffness of the trabecular meshwork3
- This may impede the outflow of aqueous humor and result in persistently high IOP3
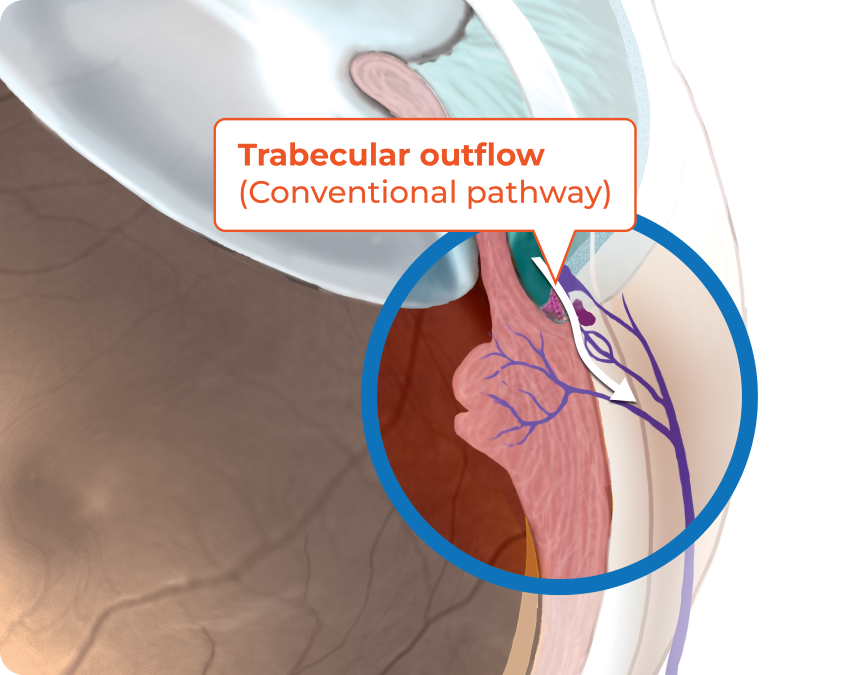
RHOPRESSA® (netarsudil ophthalmic solution) 0.02% is believed to reduce IOP by increasing the outflow of aqueous humor through the trabecular meshwork4
The exact mechanism is unknown.
IOP=Intraocular Pressure.
REFERENCES
1. Winkler NS, Fautsch MP. Effects of prostaglandin analogues on aqueous humor outflow pathways. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2014;30(2-3):102-109.
2. Saccà SC, Pulliero A, Izzotti A. The dysfunction of the trabecular meshwork during glaucoma course. J Cell Physiol. 2014;230:510-525.
3. Ren R, Li G, Duong Le T, Kopczynski C, Stamer WD, Gong H. Netarsudil increases outflow facility in human eyes through multiple mechanisms. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016;57(14):6197-6209.
4. Rhopressa® (netarsudil ophthalmic solution) 0.02% Prescribing Information, Aerie Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Irvine, CA. 2019.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Warnings and Precautions
Epithelial Corneal Edema: Epithelial Corneal Edema, described as honeycomb or bollous, has been reported in some patients with pre-existing corneal stromal edema or following ocular procedures that could affect corneal endothelial function. Epithelial corneal edema typically resolves upon discontinuation of RHOPRESSA. Advise patients to notify their physician if they experience eye pain or decreased vision while using RHOPRESSA.
Bacterial Keratitis: There have been reports of bacterial keratitis associated with the use of multiple-dose containers of topical ophthalmic products. These containers had been inadvertently contaminated by patients who, in most cases, had a concurrent corneal disease or a disruption of the ocular epithelial surface.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Rhopressa® (netarsudil ophthalmic solution) 0.02% is indicated for the reduction of elevated intraocular pressure in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension.
Contact Lenses: Contact lenses should be removed prior to instillation of Rhopressa® and may be inserted 15 minutes following its administration.
Adverse Reactions
The most common ocular adverse reaction observed in controlled clinical studies with Rhopressa® dosed once daily was conjunctival hyperemia, reported in 53% of patients. Six percent of patients discontinued therapy due to conjunctival hyperemia. Other common (approximately 20%) adverse reactions were: corneal verticillata, instillation site pain, and conjunctival hemorrhage. Instillation site erythema, corneal staining, blurred vision, increased lacrimation, erythema of eyelid, and reduced visual acuity were reported in 5-10% of patients.
The corneal verticillata seen in Rhopressa®- treated patients were first noted at 4 weeks of daily dosing. This reaction did not result in any apparent visual functional changes. Most corneal verticillata resolved upon discontinuation of treatment.
Please click here for full prescribing information for Rhopressa®.
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit www.fda.gov/medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended dosage is one drop in the affected eye(s) once daily in the evening.
